Physics Made Easy: your Support hub
Your Physics Transformation Starts Here!
Ever wondered what truly lights up our homes, powers your smartphone, or makes a car engine purr? It’s not magic—though for centuries, it certainly seemed like it. Welcome to the captivating story of electric current: the silent, invisible force that transformed our world.
Picture this: a world where lightning was considered the wrath of gods, and static shocks were merely amusing parlor tricks. For millennia, humanity lived in darkness after sunset, communicated at the speed of a galloping horse, and powered machinery with nothing but steam and muscle.
Yet whispers began circulating about a mysterious force:
These phenomena fascinated and baffled scientists and society alike. What was this mysterious élan vital? Was it a fluid, a spirit, or some unknown force? Could it possibly be harnessed?
The answers—as often happens in science—emerged from a captivating blend of curiosity, spectacular failures, and astonishing breakthroughs.

Ancient Greeks knew that rubbing amber (elektron) could attract light objects. But this was just static electricity—a momentary charge. The idea of continuous flow, a true current, was still centuries away.
The real quest began in the late 18th century with a rather unexpected hero: Luigi Galvani, an Italian physician working at the University of Bologna.
Starting around 1780, Galvani made a peculiar observation during his experiments. Beginning his studies on November 6th, 1780 (documented in his lab notebook), he witnessed something extraordinary: frog legs twitched violently when touched by two different metals.
Galvani’s conclusion? He called this “animal electricity,” believing the animals themselves generated this vital fluid.
Plot twist: His interpretation was wrong, but his observation was revolutionary!
Alessandro Volta, a brilliant Italian physicist, was intrigued by Galvani’s dancing frogs but deeply skeptical of “animal electricity.” His radical theory? The electricity came from the metals themselves when in contact with a moist conductor.
This distinction was absolutely critical!
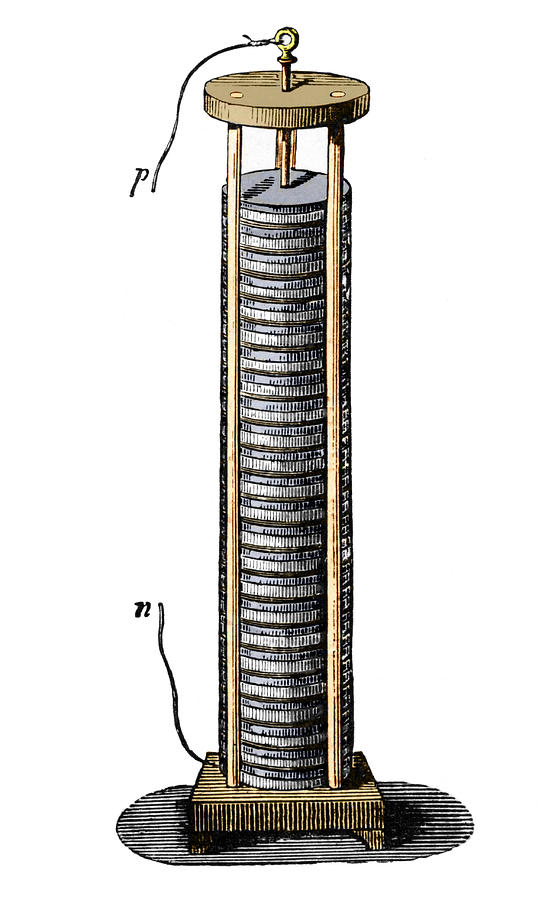
Through relentless experimentation and countless “failed” attempts that only refined his understanding, Volta created something unprecedented:
The Voltaic Pile ⚡
The result? The world’s first true battery! For the first time in human history, we had a device that could produce continuous, reliable electric current.
From fleeting spark to steady stream—humanity had tamed lightning itself.
In 1820, Danish physicist Hans Christian Ørsted was giving a lecture when serendipity struck. During a demonstration, he accidentally noticed that a compass needle twitched when he turned on an electric current nearby.
This simple observation was monumental! It proved, for the first time, a direct link between electricity and magnetism. No longer were they separate forces—they were two sides of the same coin: electromagnetism.

The ripple effects were immediate:
🧮 André-Marie Ampère (France): Within weeks, formulated mathematical laws describing forces between electric currents
🔬 Georg Ohm (Germany): In 1827, published the fundamental relationship between current, voltage, and resistance
Perhaps the most profound leap came from an unlikely source: Michael Faraday, who started as a bookbinder’s apprentice with little formal education.
In the 1830s, Faraday demonstrated something extraordinary: when a magnetic field moved through a coil of wire, it induced an electric current.
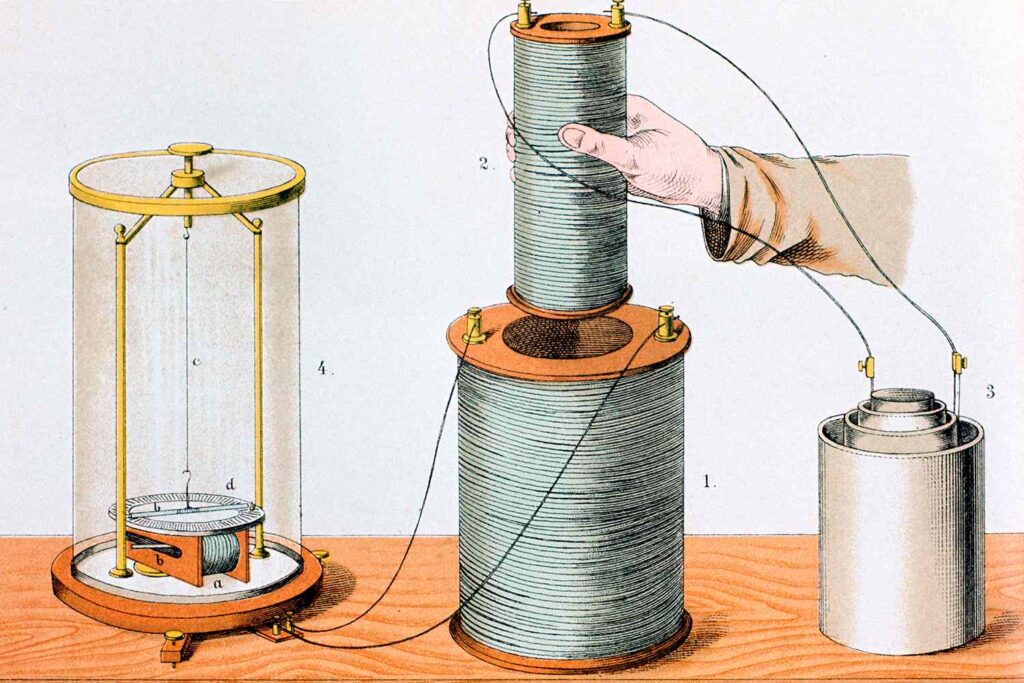
This was electromagnetic induction—the very foundation of:
If Ørsted linked electricity to magnetism, Faraday showed how magnetism could create electricity.
The journey to understanding electric current wasn’t a straight line. It was a beautifully messy testament to the scientific method:
Understanding and harnessing electric current didn’t just advance science—it revolutionized human civilization.
With steady current, Samuel Morse developed the telegraph in the 1830s:
Thomas Edison and Joseph Swan’s incandescent light bulbs (late 19th century):
Faraday’s induction principles enabled Nikola Tesla and George Westinghouse to develop:
From radio to smartphones, electric current is the lifeblood of virtually every technology:
Consider this journey: From a twitching frog leg to continuous flow… from a compass needle’s flutter to the vast interconnected grid powering our global civilization.
It’s a story of invisible forces made visible through:
Pause for a moment. You’re witnessing the legacy of curious minds who dared to ask “What if?” and “Why?“
They tamed an invisible river, transforming it into a force that:
The journey of discovery is far from over. What other invisible forces are waiting for your curious mind to unravel their secrets?
The next breakthrough might be just one “failed” experiment away…
💡 Remember: Every time you experience the convenience of modern life, you’re benefiting from centuries of brilliant minds who refused to accept “that’s just how things are.” They asked questions, failed forward, and ultimately lit up the world—literally.